r/anhedonia
Personal Wiki
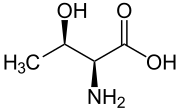
Threonine
- Research suggests that Threonine supplementation enhances hepatic lipid metabolism, reducing the risk of fat accumulation in the liver, which can lead to conditions like hepatic steatosis.
- Threonine deficiency can induce hepatic triglyceride accumulation, while supplementation exerts a protective effect by regulating lipogenesis signaling pathways and thermogenic gene expression. For example, a study on obese mice showed that Threonine supplementation restored decreased UCP1 expression, highlighting its potential in managing lipid metabolic disorders.
- Supplementing a Threonine-deficient diet in rats reduced liver fat accumulation, supporting the notion that adequate Threonine levels are crucial for preventing fatty liver (Prevention of Fatty Liver due to Threonine Deficiency by Moderate Caloric Restriction | Nature).
- Threonine's role in protein synthesis is fundamental, given its status as an essential amino acid. It is a building block for proteins, notably collagen, elastin, and enamel protein, which are critical for the structural integrity of connective tissues. This is evident from sources like Dr. Axe, which detail Threonine's involvement in forming the foundation of bones, muscles, and skin (Threonine Benefits, Uses, Foods, Supplements and Side Effects - Dr. Axe). The PMC review further elaborates that Threonine is required for synthesizing Threonine-rich proteins like mucins, with 71% of total Threonine usage in piglets dedicated to mucosal protein synthesis, underscoring its importance in tissue repair and maintenance.
- Threonine's impact on intestinal health is another significant pharmacological action, with high intestinal extraction rates (40–60% of dietary intake) used for mucosal protein synthesis and oxidation. The PMC article provides detailed insights, noting that Threonine maintains mucosa integrity, enhances villus height, and affects digestive enzyme synthesis, with specific demands like 11% of total protein for amylase synthesis in broilers. It also plays a role in gut microbiota, reducing pathogenic bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli while increasing beneficial microbes like Lactobacillus, as seen in studies with dietary Threonine levels 26% above NRC recommendations.
- Moreover, Threonine supports immune function within the gut, comprising 7–11% of IgA and modulating cytokine expression via pathways like MAPK and TOR. For instance, it up-regulates IL-6 in piglets and affects mRNA expression of immune-related genes, suggesting a role in enhancing gastrointestinal immune responses (Physiological Functions of Threonine in Animals: Beyond Nutrition Metabolism).
- Threonine serves as a precursor to other amino acids, notably glycine and serine, which have their own physiological roles. This is highlighted in DrugBank, where it is noted that Threonine is changed in the body to glycine, potentially reducing muscle contractions, though evidence for clinical benefits is limited (DrugBank Online: Threonine). The Wikipedia entry also mentions its use in synthesizing glycine for L-carnitine production in the brain and liver, particularly in rats, indicating a broader metabolic role (Threonine - Wikipedia).
- While there is interest in Threonine's potential for neurological conditions like ALS and multiple sclerosis, current evidence does not strongly support its effectiveness. WebMD notes that taking Threonine by mouth does not slow ALS progression or reduce symptoms, and there is insufficient reliable information for other uses, suggesting a need for further research (WebMD: Threonine).
- An unexpected detail is Threonine's role in cell proliferation and epigenetic regulation, particularly in embryonic stem cells (ESCs). The PMC review details that Threonine is necessary for the undifferentiated state and proliferation of mouse ESCs, with TDH mRNA levels 1000 times higher in ESCs than in differentiated cells. It also participates in histone methylation via Thr catabolism, maintaining the pluripotent state by affecting H3K4 di- and trimethylation, which could have implications for regenerative medicine and tissue repair.
Action Category Description Supporting Evidence Liver Health Aids fat metabolism, prevents hepatic fat accumulation PMC review, Nature study, DrugBank Protein Synthesis Essential for collagen, elastin, and mucin synthesis Dr. Axe, PMC review, DrugBank Intestinal Health Supports mucin production, enhances gut barrier, reduces pathogens PMC review, Nutrivore, ScienceDirect articles Immune Modulation Enhances gut immune responses, modulates cytokine expression PMC review, studies on broilers and piglets Precursor Role Precursor to glycine and serine, supports metabolic pathways DrugBank, Wikipedia Cell Proliferation Necessary for ESC proliferation, affects epigenetic regulation PMC review, unexpected in clinical pharmacology context Neurological Potential Limited evidence for ALS, MS; speculative for mental health WebMD, DrugBank, no strong clinical support