r/anhedonia
Personal Wiki
Alanine
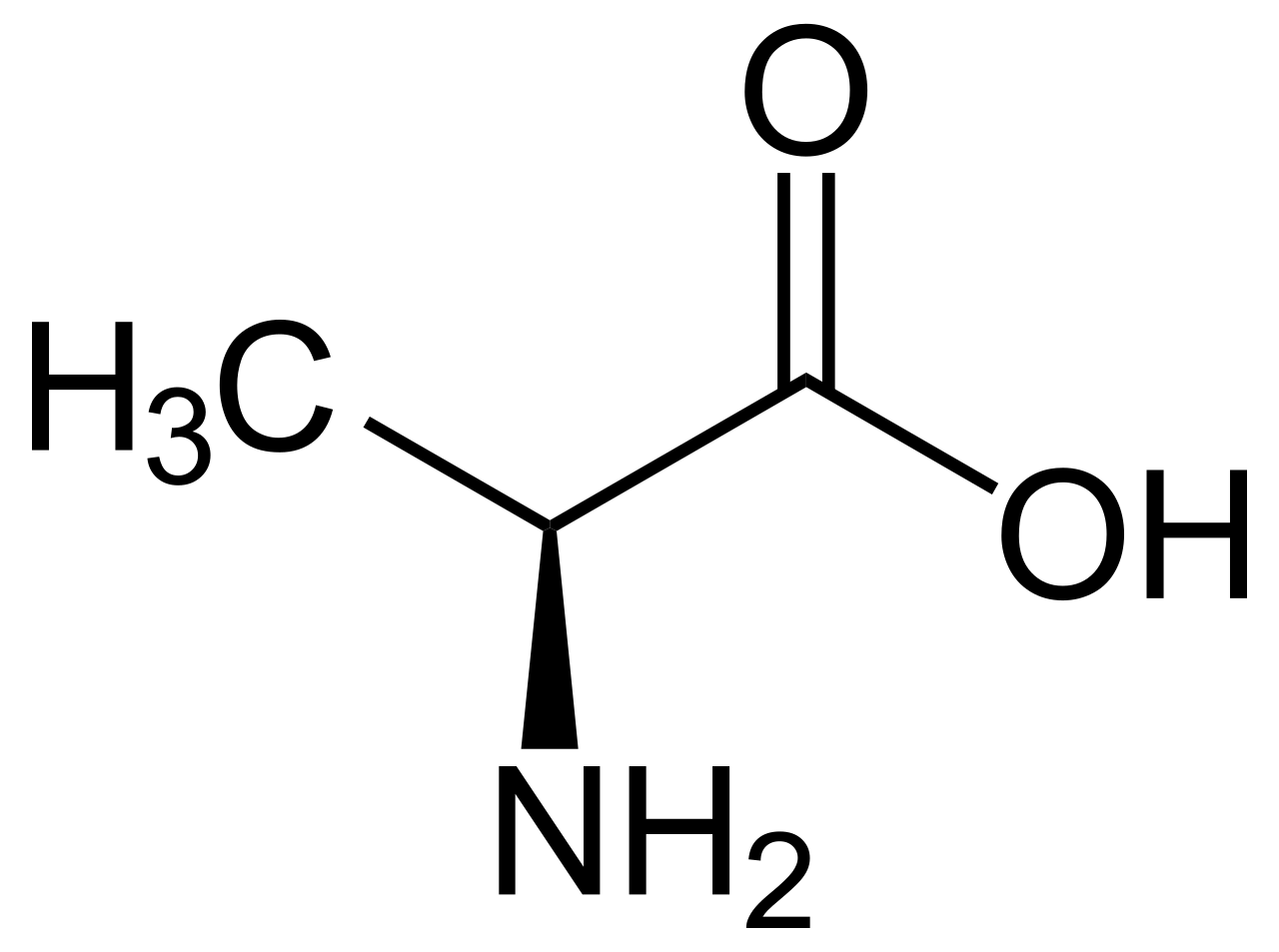
- Blood Sugar Regulation
- Essential amino acids for protein synthesis and energy
- Supports the immune system, though the exact mechanisms are not fully clear.
- Agonist at the NMDA-glycine site.
- Is a glucogenic amino acid, meaning it can be converted into glucose in the liver through gluconeogenesis.
- L-alanine is released from muscle tissues during protein breakdown and transported to the liver, where it undergoes transamination via alanine transaminase (ALT), producing pyruvate. Pyruvate is then converted into glucose, contributing to blood glucose homeostasis and preventing hypoglycemia, especially in glucose-dependent tissues like the brain and red blood cells.
- Care must be taken, as it can be harmful if blood sugar is already normal or high, necessitating careful monitoring.
- It serves as an energy source for muscles and the central nervous system.
- It is often used in combination with other amino acids, such as in alanine-glutamine dipeptides, to enhance solubility and stability in nutritional solutions.
- An unexpected and less commonly discussed aspect is the pharmacological action of D-alanine, the enantiomer of L-alanine. D-alanine is a selective and potent agonist at the NMDA-glycine site, a receptor involved in excitatory neurotransmission. Research has shown it improves cognition and negative symptoms in schizophrenia, particularly when used alongside antipsychotics, with a small randomized controlled trial (n=22) demonstrating benefits without significant side effects (Alanine).
- Alanine also has structural roles in proteins, with 31 residues in the I2S structure, and mutations at alanine sites can lead to disease phenotypes. For example, mutations like p.Ala68Glu, p.Ala85Ser, and p.Ala205Thr are associated with severe or attenuated phenotypes, depending on their location (mid-helix or buried positions) (Studie).
Action Mechanism Clinical Relevance Gluconeogenesis Support Converted to glucose via ALT in liver, part of glucose-alanine cycle Manages hypoglycemia, supports fasting/exercise states Nutritional Support Provides amino acids for protein synthesis, energy source Used in total parenteral nutrition, critical illness care Immune System Support Contributes to immune function, often in dipeptides like alanine-glutamine Potential in reducing infections, improving patient outcomes NMDA Agonist (D-alanine) Agonist at NMDA-glycine site, improves cognition in schizophrenia Investigational for neurological disorders, not for depression Structural Role and Disease Mutations affect protein stability, linked to disease phenotypes Informative for genetic and therapeutic research